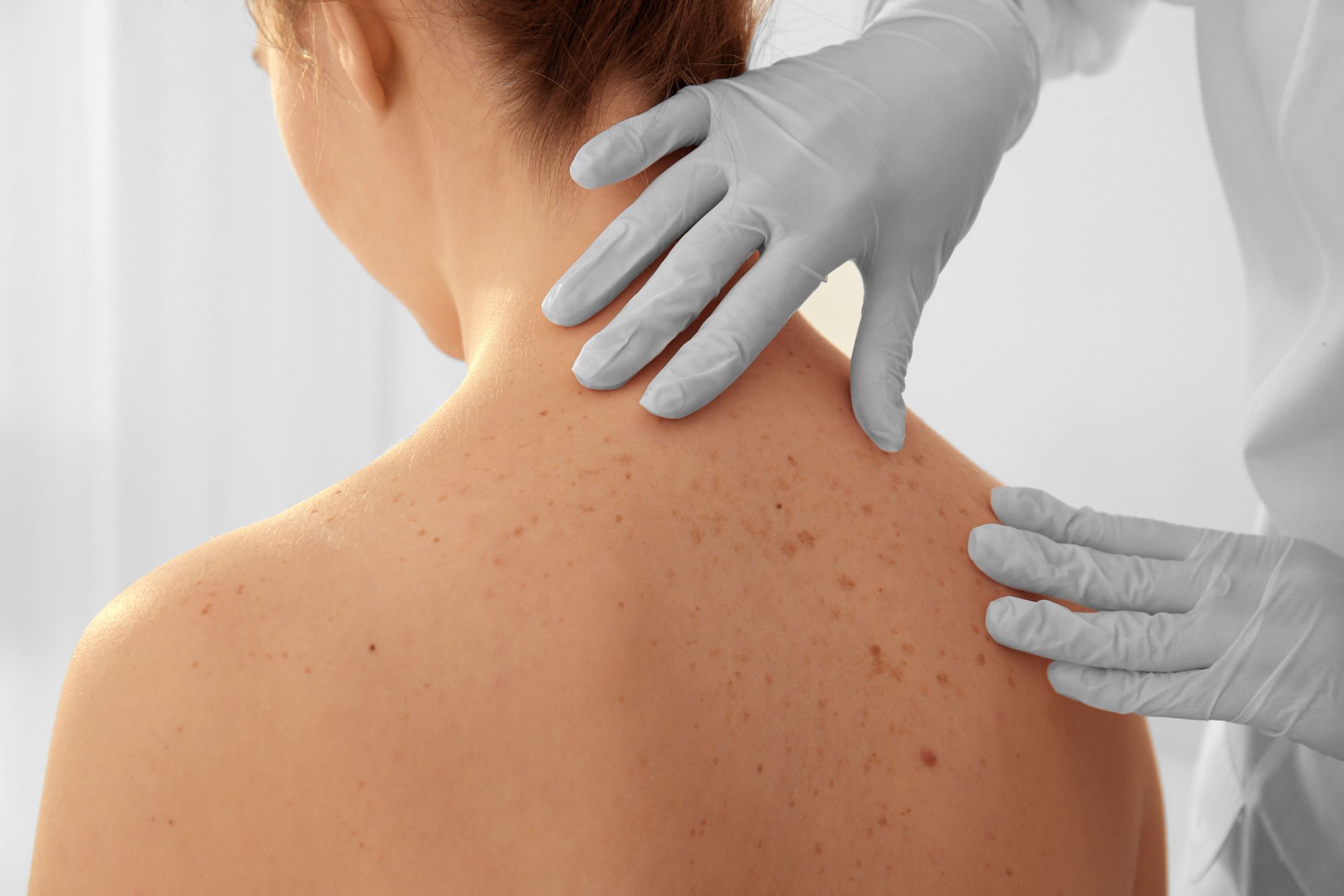
What Is Melanoma?
Melanoma is the least common skin cancer, but causes the majority of skin cancer deaths.
What makes melanoma so deadly is its ability to metastasize in three different ways: through the skin, blood and lymphatics.
As opposed to basal and squamous cell carcinoma tendencies to stay localized, melanoma’s ability to spread through the blood makes it particularly dangerous.
However, melanoma is highly curable when found in the beginning stages, which makes early detection key for treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of Melanoma?
Even though melanoma most commonly appears as a changing mole — one that’s growing larger and darker — it is critical to perform monthly self-exams to catch these changes before it’s too late.
Some patients are unsure of what to look for, but an easy way to assess early features of melanoma is to use the “ABCDE” checklist.
Asymmetry: If you drew a line down the middle, the sides would not match.
Border: The edges of the spot are ragged, notched, or blurred, and the pigment appears to fade into the skin.
Color: The color is not uniform and contains shades of black, brown, and tan (and maybe white, gray, red, pink, or blue).
Diameter: Melanoma can range in size, but most are larger than six millimeters in diameter.
Evolving: Look for changes in the spot over several weeks or months.
If you have a mole that meets any of the “ABCDE” criteria, it’s vital to see your dermatologist immediately.
What Causes Melanoma?
The causes of melanoma are not as clear as other skin cancers like basal and squamous cell carcinoma.
There’s a clear component of UV-induced damage that drives genetic changes towards melanoma. Exposure to the sun or even artificial rays from indoor tanning beds, drastically increases the potential for developing melanoma.
However, melanoma can also arise in areas that are completely sun-protected due to a genetic predisposition.
What Are the Treatment Options for Melanoma?
Despite the numerous options for melanoma treatment, surgery is usually our first preference. If possible, we’ll remove the spot completely.
Mohs Surgery for Melanoma
Mohs surgery is a treatment option for certain stages of melanoma. Mohs surgery for melanoma in situ, which is often found on the face, allows us to remove the minimal amount of tissue while even more effectively removing the tumor. We’re even using Mohs for deeper, more invasive melanomas.
Years ago, the removal of a melanoma tumor included taking a five-centimeter margin around the tumor to best prevent recurrence. We can now take only a few millimeters around these melanomas when Mohs is done in conjunction with special stains, and the cure rates are increasing.
Learn more about Mohs surgery for Melanoma.
Additional Treatment Options for Melanoma:
In cases where Mohs surgery may not be an option, your dermatologist can discuss alternative treatment options including:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Biological therapy
- Targeted therapy
FAQ’s About Melanoma
Why is Mohs surgery the first option for melanoma?
First developed to treat non-melanoma skin cancers, Mohs surgery is now used for melanoma because it’s highly effective, tissue-sparing, and offers a quick recovery with excellent cosmetic results.
How do I perform a monthly self-exam?
Monthly skin exams should be done in front of a full-length mirror with good lighting and a small hand mirror to check hard to see places. You can also ask a trusted friend or family member to assist you if needed.
How can I reduce my chances for melanoma?
Preventing sun damage is the number one way to prevent melanoma from developing. You can do that by wearing sunscreen every day and wearing protective clothing during extended time in the sun.
For people with a family history of melanoma, there are now genetic tests available. You can be screened for known genetic defects that predispose you to the development of melanoma. If these are found, you and your doctor can be on high alert for early detection of these spots.
Additional Resources
- What You Need to Know About Melanoma: A Comprehensive Guide
- What to Look For: The ABCDE’s of Skin Cancer
- Freckle or Skin Cancer? When You Should Be Worried About Your Skin Spots
Click here to find an Epiphany provider near you.